Rtv room temperature vulcanized cures under which of these conditions – RTV room temperature vulcanized curing, a process that has revolutionized various industries, presents a fascinating realm of material science. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of RTV curing, exploring the conditions under which it occurs and its wide-ranging applications.
RTV curing involves the cross-linking of polymers at room temperature, offering unique advantages in terms of flexibility, adhesion, and ease of use. Understanding the conditions that govern this process is crucial for achieving optimal results and unlocking the full potential of RTV materials.
1. RTV Room Temperature Vulcanized Curing Conditions: Rtv Room Temperature Vulcanized Cures Under Which Of These Conditions
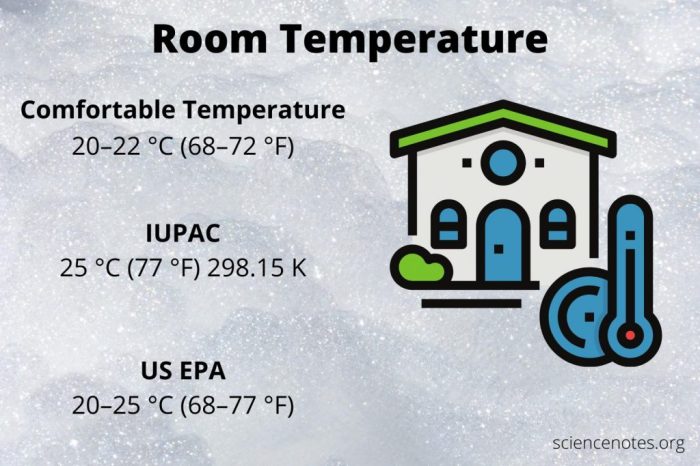
Room temperature vulcanization (RTV) is a curing process for elastomers and silicones that occurs at ambient temperature, typically between 20°C and 25°C. RTV curing involves the cross-linking of polymer chains to form a solid, elastic material. This process is widely used in various industries due to its simplicity, versatility, and ability to produce high-quality elastomeric products.
RTV curing conditions play a crucial role in determining the properties of the cured material. The following are the primary conditions that influence RTV curing:
- Temperature:The ideal curing temperature for RTV materials ranges from 20°C to 25°C. Deviations from this range can affect the curing rate and the final properties of the cured material.
- Humidity:Moisture in the air can act as a catalyst for RTV curing. Controlled humidity levels are essential to ensure consistent curing and prevent premature or incomplete curing.
- Catalyst Concentration:The addition of a catalyst to the RTV material initiates and accelerates the curing process. The concentration of the catalyst influences the curing time and the properties of the cured material.
- Curing Time:The curing time for RTV materials varies depending on the specific formulation and the curing conditions. Longer curing times generally result in higher cross-linking density and improved material properties.
2. Applications of RTV Curing

RTV curing finds applications in a wide range of industries and products, including:
- Automotive:RTV silicones are used as sealants, gaskets, and adhesives in automotive components, such as engines, transmissions, and body panels.
- Electronics:RTV materials are employed as encapsulants and protective coatings for electronic components, providing insulation, moisture resistance, and vibration damping.
- Construction:RTV sealants are used to fill gaps, seal joints, and provide weatherproofing in construction applications, such as roofing, glazing, and plumbing.
- Medical:RTV silicones are used in medical devices, such as catheters, implants, and prosthetics, due to their biocompatibility, flexibility, and resistance to sterilization.
- Aerospace:RTV materials are utilized in aerospace applications, such as aircraft seals, fuel tanks, and thermal insulation, due to their lightweight, high-temperature resistance, and vibration damping properties.
The advantages of using RTV curing in these applications include its versatility, ease of application, ability to conform to complex shapes, and the production of durable and reliable products.
Popular Questions
What are the key factors that influence RTV curing?
The curing time, temperature, humidity, and presence of catalysts or inhibitors can significantly affect the rate and extent of RTV curing.
What are the advantages of using RTV curing?
RTV curing offers advantages such as low-temperature processing, fast curing times, and excellent adhesion to various substrates.
What are some common applications of RTV materials?
RTV materials are widely used in sealants, adhesives, coatings, and molding applications across industries such as automotive, electronics, and construction.