A process called converts vector graphics into bitmap images – Rasterization, a process that converts vector graphics into bitmap images, plays a crucial role in the digital world. This transformation enables the display and manipulation of images on various platforms, from web pages to print media. This comprehensive overview delves into the fundamentals of rasterization, exploring its advantages, disadvantages, applications, and future prospects.
Rasterization Process

Rasterization is the process of converting vector graphics into bitmap images. Vector graphics are defined by mathematical equations that describe shapes and lines, while bitmap images are composed of individual pixels. Rasterization involves converting these mathematical equations into a grid of pixels, allowing them to be displayed on raster devices such as computer monitors and printers.
Transformation of Vector Graphics into Bitmap Images
The rasterization process begins by sampling the vector graphic at specific intervals, creating a grid of pixels. Each pixel is then assigned a color based on the color of the vector graphic at that point. This process continues until the entire vector graphic has been converted into a bitmap image.
Role of Pixels
Pixels are the fundamental building blocks of raster images. They are tiny square dots that represent a single point in the image. The size and arrangement of pixels determine the resolution and quality of the raster image. Higher resolutions result in more pixels and finer detail, while lower resolutions result in fewer pixels and a coarser appearance.
Advantages of Rasterization
Benefits in Image Display and Manipulation
Rasterization offers several advantages for image display and manipulation. Raster images can be displayed on a wide range of devices, including computer monitors, TVs, and smartphones. They can also be easily edited and manipulated using image editing software, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
Suitability for Specific Applications
Raster images are particularly well-suited for applications that require high-resolution images, such as digital photography, graphic design, and printing. They are also commonly used in web design and user interfaces due to their compatibility with various web browsers and devices.
Examples of Advantages in Various Industries
- Digital photography:Raster images allow photographers to capture and store high-resolution images with accurate color reproduction.
- Graphic design:Raster images provide designers with the flexibility to create complex and detailed artwork for print and digital media.
- Printing:Raster images are used in printing to produce high-quality images for brochures, posters, and other printed materials.
Disadvantages of Rasterization: A Process Called Converts Vector Graphics Into Bitmap Images

Limitations and Drawbacks, A process called converts vector graphics into bitmap images
Rasterization also has some limitations and drawbacks. Raster images can be large in file size, especially for high-resolution images. They can also lose quality when scaled or resized, resulting in pixelation and loss of detail.
Loss of Image Quality When Scaling or Resizing
When a raster image is scaled up, the pixels become more visible, resulting in a loss of sharpness and detail. Conversely, when a raster image is scaled down, pixels are combined, which can lead to a loss of color accuracy and a blocky appearance.
Potential Challenges in Editing or Manipulating Raster Images
Editing or manipulating raster images can be challenging due to the fixed nature of pixels. It can be difficult to make precise adjustments or remove unwanted elements without affecting the surrounding pixels.
Applications of Rasterization
| Industry | Purpose | Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Web design | Displaying images on websites | Product images, banner ads, social media graphics | Compatibility with web browsers, ease of editing |
| Digital photography | Capturing and storing high-resolution images | Landscape photography, portraits, wildlife photography | Accurate color reproduction, flexibility in post-processing |
| Printing | Producing high-quality printed materials | Brochures, posters, billboards | Vivid colors, sharp details, suitability for various printing techniques |
| User interfaces | Creating visual elements for apps and websites | Icons, buttons, menus | Intuitive design, easy customization, cross-platform compatibility |
Comparison with Vector Graphics
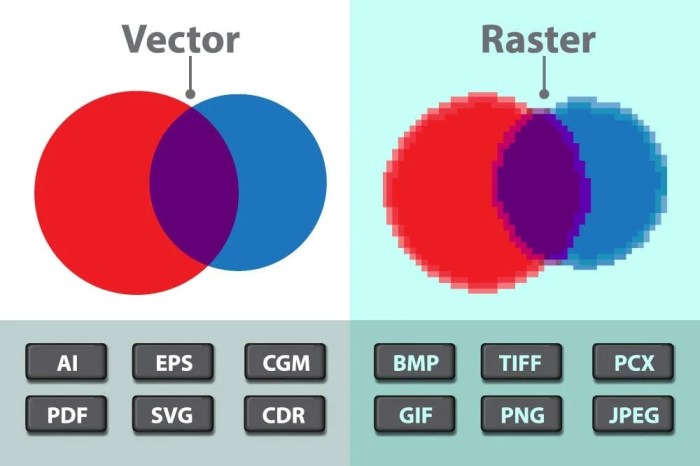
| Property | Raster Graphics | Vector Graphics |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pixels | Mathematical equations |
| Scalability | Loss of quality when scaled | No loss of quality when scaled |
| File size | Larger file sizes | Smaller file sizes |
| Editing | Challenging to edit | Easy to edit |
| Applications | High-resolution images, digital photography, printing | Logos, illustrations, icons |
Future of Rasterization
Rasterization technology continues to evolve, driven by advancements in AI and machine learning. These advancements are enabling the development of new techniques for improving the quality and efficiency of rasterization. For example, AI-powered algorithms can be used to optimize pixel placement and color reproduction, resulting in more realistic and detailed images.
The future of rasterization also lies in its integration with emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). Raster images can be used to create immersive and interactive experiences, allowing users to interact with virtual environments and objects.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the primary advantage of rasterization?
Rasterization allows for the efficient display and manipulation of images on digital devices, making it suitable for web design, digital photography, and printing.
What is a key limitation of raster images?
Raster images can lose quality when scaled or resized, as they are composed of a fixed number of pixels.
How is rasterization used in web design?
Raster images are commonly used in web design to display photographs, logos, and other visual elements on web pages.