AP Physics 1 Circular Motion and Gravitation Test Answers: A Comprehensive Guide delves into the captivating realm of physics, providing a comprehensive overview of circular motion and gravitation concepts. This guide empowers students with a thorough understanding of these fundamental principles, equipping them with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in their AP Physics 1 exam.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the intricacies of circular motion, examining its characteristics and the relationship between centripetal force and centripetal acceleration. We will also delve into the concept of gravitation, investigating its properties and the applications of the law of universal gravitation.
By delving into real-world examples and practice questions, this guide aims to foster a deep understanding of these concepts and enhance students’ problem-solving abilities.
AP Physics 1 Circular Motion
Circular motion is the movement of an object along a circular path. It is characterized by a constant speed and a changing direction of velocity. Examples of circular motion include the motion of a planet around the sun, the motion of a car around a curve, and the motion of a yo-yo as it swings.
The force that causes an object to move in a circular path is called the centripetal force. The centripetal force is always directed towards the center of the circle. The centripetal acceleration is the acceleration of an object moving in a circular path.
The centripetal acceleration is always directed towards the center of the circle.
Relationship between Centripetal Force and Centripetal Acceleration
The centripetal force and the centripetal acceleration are related by the following equation:
Fc= m
ac
where:
- F cis the centripetal force
- m is the mass of the object
- a cis the centripetal acceleration
AP Physics 1 Gravitation
Gravitation is the force of attraction between two objects. The force of gravity is always attractive and it is proportional to the mass of the objects. The force of gravity is also inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the objects.
The law of universal gravitation states that the force of gravity between two objects is given by the following equation:
Fg= G
- m 1
- m 2/ r 2
where:
- F gis the force of gravity
- G is the gravitational constant (6.674 × 10 -11N m 2/ kg 2)
- m 1is the mass of the first object
- m 2is the mass of the second object
- r is the distance between the centers of the two objects
Examples of Gravitational Forces in Everyday Life
- The force of gravity between the Earth and the moon keeps the moon in orbit around the Earth.
- The force of gravity between the Earth and the sun keeps the Earth in orbit around the sun.
- The force of gravity between two people causes them to be attracted to each other.
Test Preparation
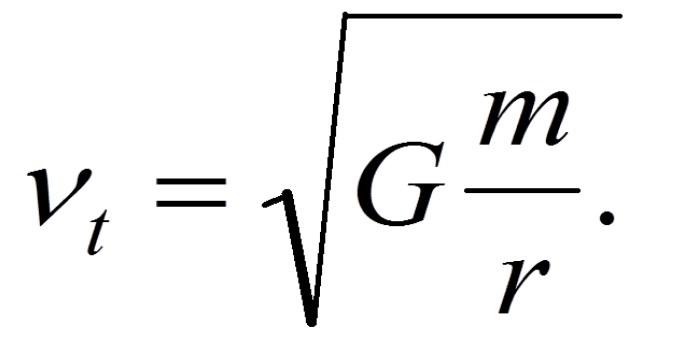
Key Concepts and Formulas
- Circular motion: speed, velocity, centripetal force, centripetal acceleration
- Gravitation: force of gravity, law of universal gravitation
Sample Questions and Solutions, Ap physics 1 circular motion and gravitation test answers
- A car is traveling around a curve with a radius of 100 m. The car’s speed is 20 m/s. What is the centripetal force acting on the car?
- Two objects have masses of 1 kg and 2 kg, respectively. The distance between the centers of the two objects is 1 m. What is the force of gravity between the two objects?
Strategies for Effective Test-Taking
- Review the key concepts and formulas.
- Practice solving problems.
- Get a good night’s sleep before the test.
- Arrive at the test early.
- Read the instructions carefully.
- Show all of your work.
Essential FAQs: Ap Physics 1 Circular Motion And Gravitation Test Answers
What is the relationship between centripetal force and centripetal acceleration?
Centripetal force is the force that acts towards the center of a circular path, causing an object to move in a circle. Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration of an object moving in a circular path, directed towards the center of the circle.
The centripetal force is directly proportional to the centripetal acceleration and the mass of the object.
How is the law of universal gravitation applied in everyday life?
The law of universal gravitation is applied in various everyday situations, such as determining the weight of objects on Earth, calculating the trajectory of projectiles, and understanding the motion of celestial bodies. It is also used in engineering applications, such as designing bridges and rockets.