A nurse is assessing an infant who has aortic stenosis, a critical congenital heart defect that affects the aortic valve. This assessment involves a thorough physical examination, medical history review, and diagnostic testing to determine the severity of the stenosis and guide appropriate treatment.
Understanding the clinical presentation, risk factors, diagnostic modalities, and treatment options for aortic stenosis in infants is crucial for nurses to provide optimal care and support to affected infants and their families.
Patient Assessment

Assessing an infant with aortic stenosis involves a comprehensive physical examination to evaluate the infant’s overall health and identify any signs or symptoms indicative of the condition.
Physical Examination Techniques
- Auscultation:Listening to the infant’s heart for abnormal heart sounds, such as a systolic murmur or a gallop rhythm.
- Palpation:Feeling the infant’s chest for a palpable thrill, which may indicate turbulent blood flow through the stenotic valve.
- Percussion:Tapping the infant’s chest to assess for an enlarged heart or pleural effusion.
Signs and Symptoms, A nurse is assessing an infant who has aortic stenosis
- Cyanosis:Bluish discoloration of the skin, especially around the lips and nail beds, due to reduced oxygen saturation.
- Tachypnea:Rapid breathing due to increased effort to compensate for reduced cardiac output.
- Failure to thrive:Poor weight gain or growth retardation due to inadequate oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Diaphoresis:Excessive sweating due to increased metabolic activity and compensatory mechanisms.
| Assessment Technique | Normal Findings | Abnormal Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Auscultation | Soft, regular heart sounds | Systolic murmur, gallop rhythm |
| Palpation | No palpable thrill | Palpable thrill over the aortic area |
| Percussion | Normal heart size | Enlarged heart, pleural effusion |
Medical History and Risk Factors: A Nurse Is Assessing An Infant Who Has Aortic Stenosis
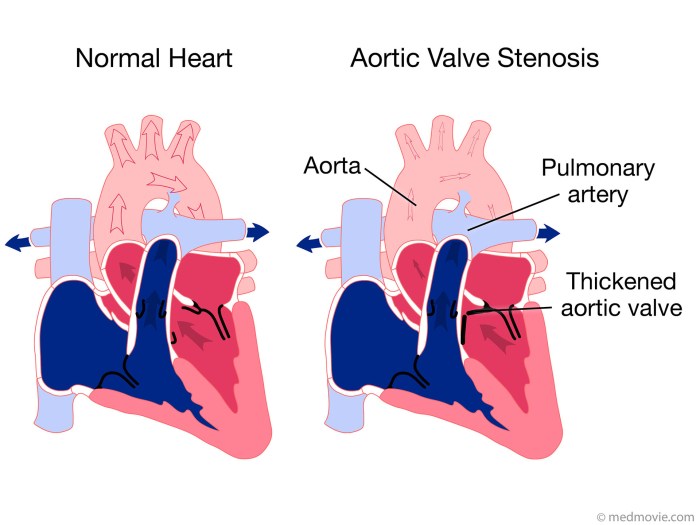
Understanding the medical history and risk factors associated with aortic stenosis in infants is crucial for early detection and management.
Common Causes
- Congenital heart defects:Aortic stenosis is often associated with other congenital heart defects, such as bicuspid aortic valve or coarctation of the aorta.
- Rheumatic fever:A rare cause in infants, but can lead to aortic valve damage and stenosis.
Prenatal Factors and Family History
- Maternal rubella infection:Rubella infection during pregnancy can increase the risk of congenital heart defects, including aortic stenosis.
- Family history of aortic stenosis:Having a first-degree relative with aortic stenosis increases the risk of developing the condition.
Risk Factors
- Premature birth:Infants born prematurely have a higher risk of developing congenital heart defects.
- Low birth weight:Infants with low birth weight are more likely to have heart defects.
- Genetic syndromes:Certain genetic syndromes, such as Williams syndrome and Turner syndrome, are associated with an increased risk of aortic stenosis.
Diagnostic Tests

Diagnostic tests are essential for confirming the diagnosis of aortic stenosis in infants and assessing the severity of the condition.
Imaging Techniques
- Echocardiography:A non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart. It can visualize the aortic valve, assess its structure and function, and measure the severity of stenosis.
- Cardiac catheterization:An invasive procedure that involves threading a catheter through the blood vessels to the heart. It can provide precise measurements of pressure gradients across the aortic valve and assess the anatomy of the valve and surrounding structures.
| Test | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Echocardiography | Non-invasive, readily available, can be repeated as needed | May not provide detailed enough information in some cases |
| Cardiac catheterization | Provides precise measurements, can assess valve anatomy | Invasive, carries risks of complications |
Essential FAQs
What are the common signs and symptoms of aortic stenosis in infants?
Infants with aortic stenosis may exhibit symptoms such as difficulty breathing, poor feeding, failure to thrive, and a heart murmur.
What is the role of echocardiography in diagnosing aortic stenosis?
Echocardiography is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart. It is commonly used to visualize the aortic valve and assess the severity of stenosis.
What are the surgical and non-surgical treatment options for aortic stenosis in infants?
Surgical options include balloon valvuloplasty and open-heart surgery to repair or replace the aortic valve. Non-surgical options may involve medications to manage symptoms and regular monitoring.