Mendelian genetics dihybrid fruit fly cross, a cornerstone of modern genetics, unveils the intricate mechanisms governing the transmission of traits across generations. This groundbreaking research, pioneered by Gregor Mendel, laid the foundation for understanding the fundamental principles of inheritance, shaping our comprehension of biological diversity and genetic disorders.
Through meticulously designed experiments involving fruit flies, Mendel uncovered the laws of inheritance, providing a framework for predicting the phenotypic outcomes of genetic crosses. These principles have revolutionized our understanding of genetic variation and continue to guide advancements in plant and animal breeding, medicine, and genetic counseling.
Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian genetics, the foundation of modern genetics, is the study of inheritance patterns based on the laws proposed by Gregor Mendel. Mendel’s experiments with pea plants led to the discovery of fundamental principles that govern the transmission of genetic traits from parents to offspring.
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
- Law of Segregation:Alleles for a particular gene separate during gamete formation, ensuring that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene.
- Law of Independent Assortment:Alleles for different genes assort independently of each other during gamete formation.
- Law of Dominance:When two different alleles are present in an individual, the dominant allele masks the expression of the recessive allele.
Significance of Mendel’s Work
Mendel’s work laid the groundwork for understanding the principles of inheritance. It provided a scientific basis for explaining how traits are passed down from one generation to the next, revolutionizing the field of biology.
Dihybrid Fruit Fly Cross
Experimental Setup
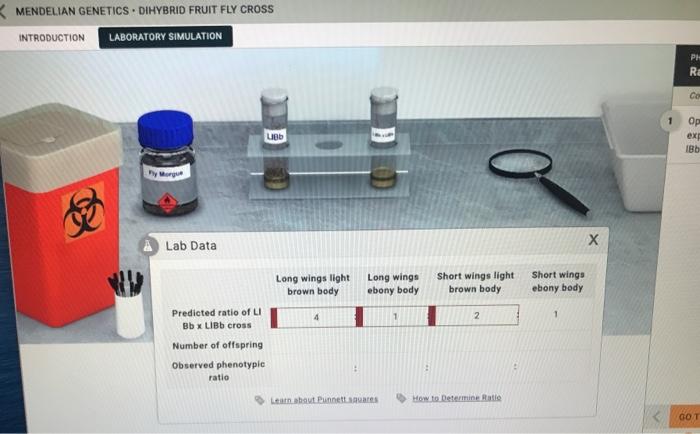
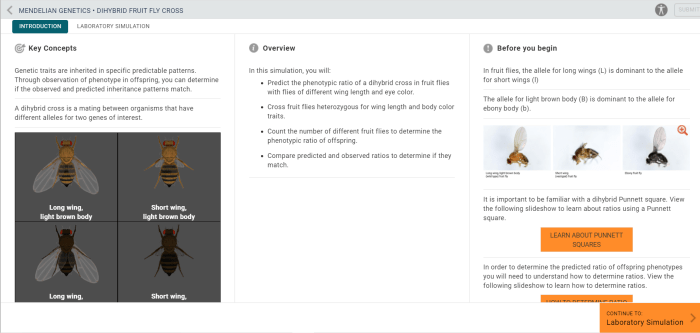
In a dihybrid cross, fruit flies with different homozygous genotypes are crossed to produce offspring that are heterozygous for both traits.
Expected Phenotypic Ratios
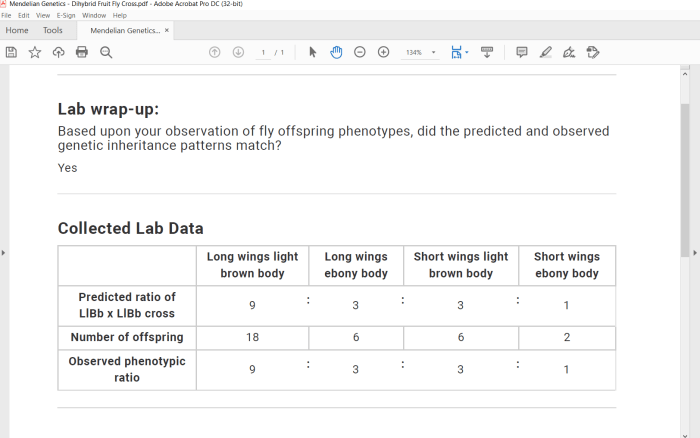
The expected phenotypic ratios from a dihybrid cross are 9:3:3:1. This ratio represents the probability of each possible genotype and phenotype in the offspring.
Punnett Square
A Punnett square is a diagram that illustrates the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a particular cross. In a dihybrid cross, the Punnett square is used to predict the probability of each possible genotype and phenotype.
Inheritance of Traits
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
In Mendelian genetics, dominant alleles are expressed in the phenotype even if only one copy is present, while recessive alleles are only expressed when two copies are present.
Heterozygosity and Homozygosity, Mendelian genetics dihybrid fruit fly cross
Individuals with two identical alleles for a particular gene are said to be homozygous for that gene. Individuals with two different alleles for a particular gene are said to be heterozygous for that gene.
Examples of Mendelian Traits
- Eye color:Brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes.
- Seed shape:Round seeds are dominant over wrinkled seeds.
- Blood type:Type A and Type B blood are dominant over Type O blood.
Applications of Mendelian Genetics: Mendelian Genetics Dihybrid Fruit Fly Cross
Plant and Animal Breeding
Mendelian genetics is used to improve crop yields and livestock quality by selective breeding for desirable traits.
Medicine
Mendelian genetics is used to study inherited diseases and develop genetic tests to identify individuals at risk.
Societal Impact
Mendelian genetics has had a profound impact on society, leading to advancements in agriculture, medicine, and our understanding of human inheritance.
User Queries
What are the key principles of Mendelian genetics?
Mendelian genetics encompasses the laws of segregation and independent assortment, which dictate the inheritance of traits through discrete units called genes.
How does a dihybrid cross differ from a monohybrid cross?
A dihybrid cross involves the inheritance of two different traits simultaneously, while a monohybrid cross focuses on a single trait.
What is the significance of the Punnett square in Mendelian genetics?
The Punnett square is a graphical tool used to predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring resulting from a genetic cross.