Embark on a scientific expedition with “Evidence for Evolution Pogil Answer Key,” where we delve into the captivating realm of evolutionary biology. This comprehensive guide unlocks the secrets of evolution, unraveling the intricate tapestry of life’s extraordinary journey.
From the groundbreaking concept of natural selection to the compelling insights offered by fossil evidence, comparative anatomy, and molecular analysis, this exploration unveils the undeniable truth that evolution has shaped the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
Evidence for Evolution: Evidence For Evolution Pogil Answer Key
Evolution is the process by which populations of living organisms change over generations. This process is driven by natural selection, which is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals with advantageous traits.
Types of Evidence for Evolution, Evidence for evolution pogil answer key
There are several types of evidence that support the theory of evolution:
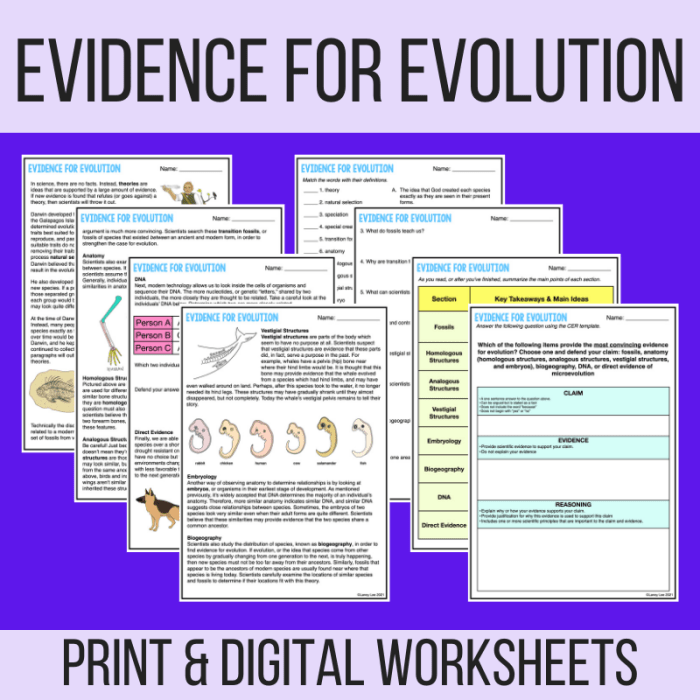
Fossil Evidence
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals, plants, and other organisms from the past. They provide a direct record of evolutionary history and can show how organisms have changed over time.
- Transitional fossils are fossils that show intermediate forms between different species, providing evidence for the gradual evolution of new species.
- Fossil evidence has limitations, such as the incompleteness of the fossil record and the potential for biases in the preservation of certain types of organisms.
Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy is the study of the similarities and differences in the anatomy of different organisms. It provides insights into evolutionary relationships:
- Homologous structures are structures that have similar form and origin in different organisms, suggesting a common ancestor.
- Analogous structures are structures that have similar function but different form and origin, suggesting convergence due to similar environmental pressures.
- Embryological development can also reveal evolutionary relationships, as organisms that share a common ancestor often go through similar stages of development.
- Vestigial structures are remnants of structures that were once functional in ancestors but have become reduced or non-functional in descendant species.
Molecular Evidence
Molecular evidence, such as DNA and protein sequences, provides powerful support for evolution:
- DNA sequencing allows scientists to compare the genetic material of different organisms and identify similarities and differences.
- DNA comparisons have been used to construct phylogenetic trees, which show the evolutionary relationships between different species.
- Molecular clocks, based on the rate of DNA mutation, can be used to estimate the time since two species diverged from a common ancestor.
Detailed FAQs
What is the fundamental principle of natural selection?
Natural selection is the driving force behind evolution, favoring individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success in a given environment.
How do fossils contribute to our understanding of evolutionary history?
Fossils provide direct evidence of past life forms, allowing us to trace the gradual changes in species over time and reconstruct the evolutionary relationships between different groups.
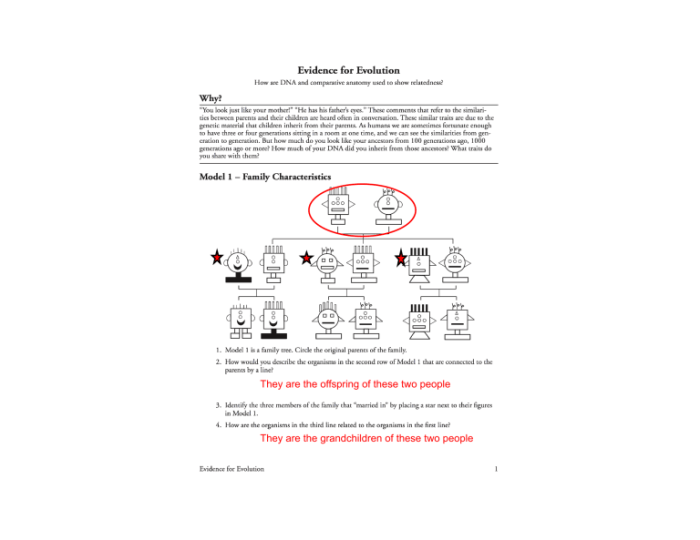
What insights can comparative anatomy offer about evolutionary relationships?
Comparative anatomy reveals striking similarities in the structures of organisms, suggesting common ancestry. These similarities, known as homologies, provide valuable clues about the evolutionary history of different species.