In a transshipment problem shipments – In the realm of logistics and supply chain management, transshipment problems present a unique set of challenges that require meticulous planning and optimization. At the heart of these problems lies the intricate network of shipments, each with its distinct characteristics and objectives.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the diverse types of shipments involved in transshipment problems, unraveling their complexities and providing practical insights into their effective management.
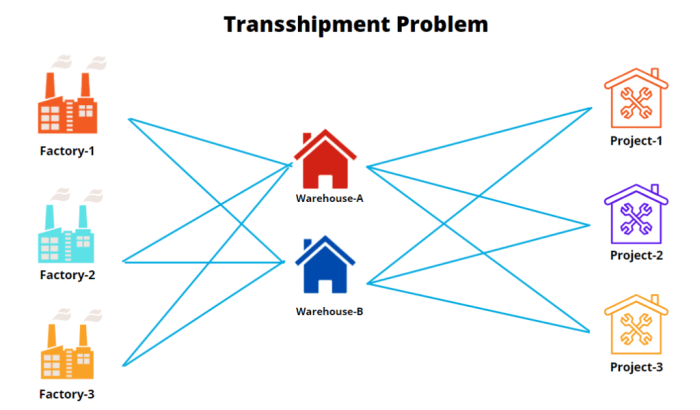
Types of Shipments in a Transshipment Problem
Transshipment problems involve different types of shipments, each with its own characteristics:
- Origin Shipments:Shipments that originate from a specific location and need to be transported to a destination.
- Destination Shipments:Shipments that are received at a specific location from an origin.
- Transshipment Shipments:Shipments that are received at an intermediate location and then forwarded to another destination.
Objectives of a Transshipment Problem
Solving a transshipment problem typically aims to achieve one or more of the following objectives:
- Minimizing Total Transportation Cost:Optimizing the total cost of transporting shipments from origins to destinations.
- Maximizing Total Flow:Ensuring that the maximum possible amount of shipments are transported from origins to destinations.
- Balancing Supply and Demand:Matching the availability of shipments at origins with the demand at destinations.
Mathematical Formulation of a Transshipment Problem
A transshipment problem can be mathematically modeled as follows: Decision Variables:
- x ij: Amount of shipment from origin i to destination j
- y ij: Amount of shipment from origin i to intermediate location j
Objective Function:
- Minimize Total Cost: ∑∑c ijx ij+ ∑∑d ijy ij
Constraints:
- Origin Supply: ∑j x ij≤ s i∀i
- Destination Demand: ∑i x ij≥ d j∀j
- Flow Conservation: ∑i y ij– ∑j y ji= ∑j x ij∀i, j
- Non-negativity: x ij, y ij≥ 0 ∀i, j
Solution Methods for Transshipment Problems: In A Transshipment Problem Shipments
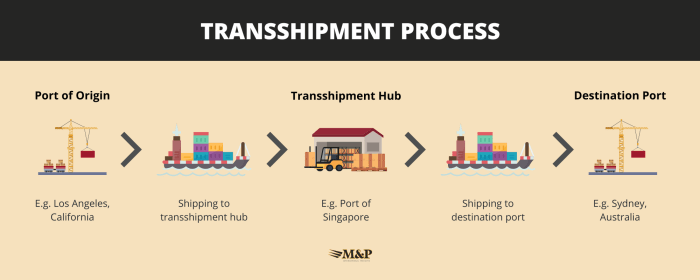
Various methods are used to solve transshipment problems:
- Network Flow Algorithms:Methods such as the Ford-Fulkerson algorithm and the Edmonds-Karp algorithm are commonly used.
- Linear Programming:Transshipment problems can be formulated as linear programming problems and solved using standard LP solvers.
- Heuristic Algorithms:Heuristic methods, such as the Clarke-Wright savings algorithm, provide approximate solutions in a reasonable amount of time.
Applications of Transshipment Problems
Transshipment problems have numerous applications in logistics and supply chain management, including:
- Distribution Planning:Optimizing the distribution of goods from warehouses to retail stores.
- Transportation Planning:Scheduling and routing of vehicles to minimize transportation costs.
- Inventory Management:Managing inventory levels at multiple locations to meet demand while minimizing holding costs.
Extensions and Variations of Transshipment Problems

Common extensions and variations of transshipment problems include:
- Multi-Commodity Transshipment Problems:Involving multiple types of commodities with different characteristics.
- Stochastic Transshipment Problems:Considering uncertainty in demand or supply.
- Dynamic Transshipment Problems:Where demand or supply changes over time.
Case Studies and Examples

Numerous case studies and examples demonstrate the successful application of transshipment problem solutions.One notable example is the implementation of a transshipment model for a global logistics company. The model optimized the distribution of goods from multiple warehouses to retail stores, resulting in significant cost savings and improved customer service.
Future Directions and Research Opportunities
Emerging trends and research directions in transshipment problems include:
- Development of more efficient algorithms:Exploring new techniques to solve large-scale transshipment problems faster and more accurately.
- Incorporation of real-time data:Integrating real-time data into transshipment models to improve decision-making.
- Applications in new domains:Extending transshipment models to solve problems in areas such as healthcare and energy distribution.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the primary objectives of solving a transshipment problem?
Minimizing transportation costs, maximizing customer service levels, and balancing supply and demand.
How does solving transshipment problems improve logistics and supply chain efficiency?
By optimizing the flow of goods through the network, reducing transportation costs, and enhancing inventory management.